|
I am an integrated MS/PhD student at Seoul National University, advised by Professor Nojun Kwak as a member of Machine Intelligence and Pattern Analysis Lab (MIPAL). My research focuses on 3D reconstruction, multi-view geometry, and neural rendering. I began my graduate work on few-shot NeRF methods, and my recent projects have shifted toward 3D Gaussian Splatting–based approaches, driven by an interest in modeling 3D reconstructions that more accurately capture real-world characteristics. My work spans relighting under natural illumination, 3D object extraction using diffusion-based inpainting, and 3D-consistent scene colorization. Prior to my graduate studies, I earned a bachelor’s degree in Astronomy and Industrial Engineering from Seoul National University. Email / CV / Google Scholar / Github |

|
|
|
|
|
Yeonjin Chang, Juhwan Cho, Seunghyeon Seo, Wonsik Shin, Nojun Kwak Under Review project page / arXiv We introduce a 3D colorization method, LoGoColor, that avoids color-averaging limitations of prior methods by generating locally and globally consistent multi-view colorized training images, enabling diverse and consistent 3D colorization for complex 360$^{\circ}$ scenes. |
|
|
Yeonjin Chang, Erqun Dong, Seunghyeon Seo, Nojun Kwak, Kwang Moo Yi Under Review project page / arXiv We introduce a 3D object extraction method for Gaussian Splatting that prunes irrelevant primitives using K-nearest neighbors analysis and compensates for occlusions with diffusion-based generative inpainting. |
|
Seunghyeon Seo, Yeonjin Chang, Jayeon Yoo, Seungwoo Lee, Hojun Lee, Nojun Kwak CVPR 2025 Workshop on Computer Vision for Metaverse (Oral) project page / arXiv We introduce ARC-NeRF, a few-shot rendering method that casts area rays to cover a broader set of unseen viewpoints, improving spatial generalization with minimal input. Alongside, we propose adaptive frequency regularization and luminance consistency loss to further refine textures and high-frequency details in rendered outputs. |
|
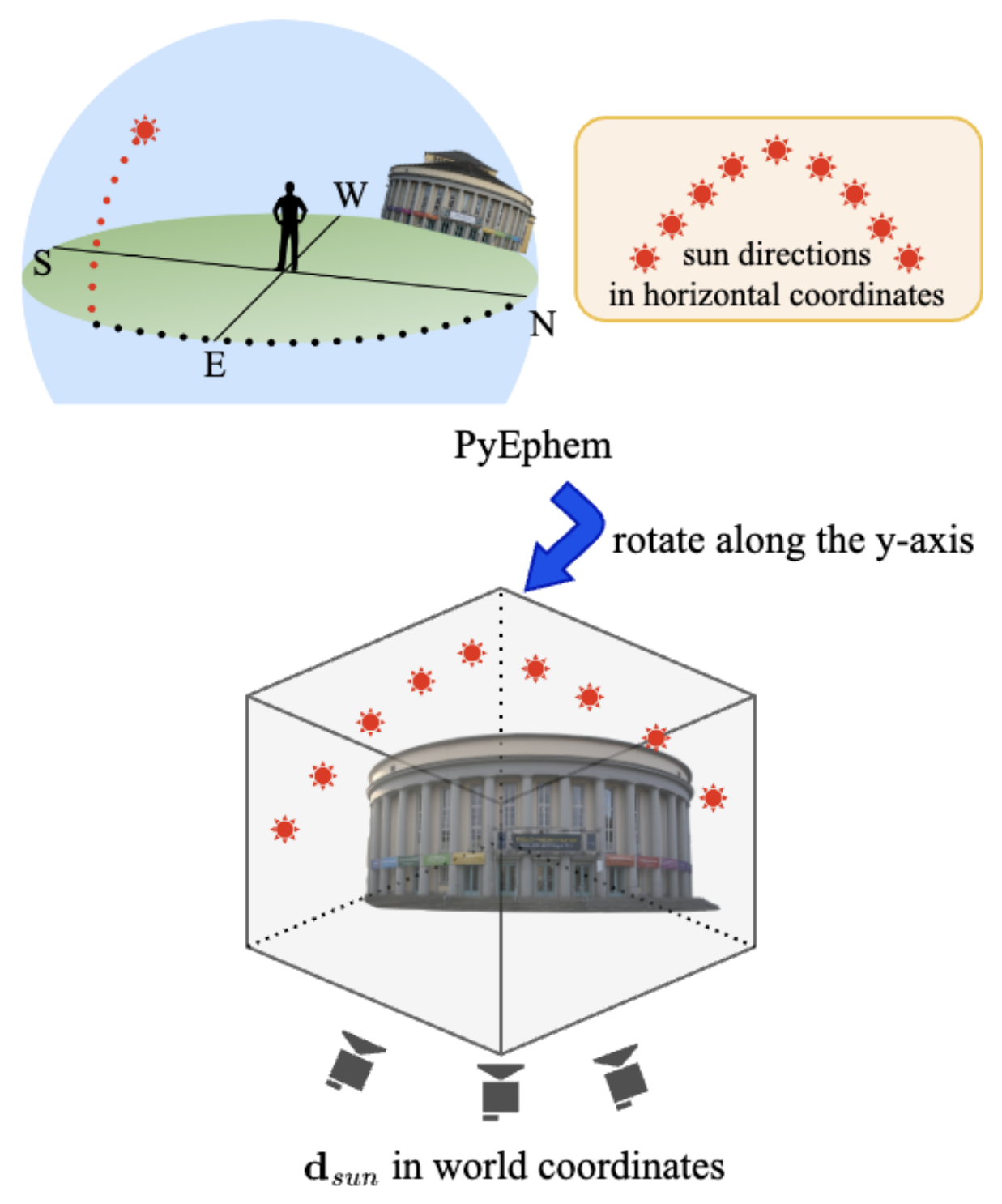
Yeonjin Chang, Yearim Kim, Seunghyeon Seo, Jung Yi, Nojun Kwak WACV 2024 arXiv We simplify outdoor scene relighting for NeRF by aligning with the sun, eliminating the need for environment maps and speeding up the process using a novel cubemap concept within the framework of TensoRF. |
|
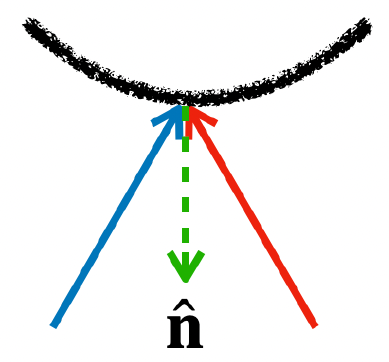
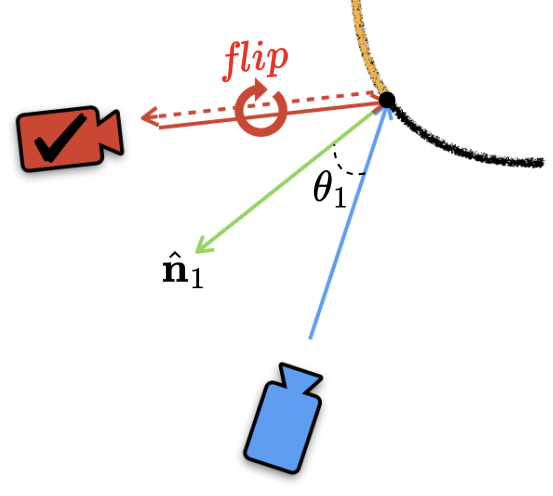
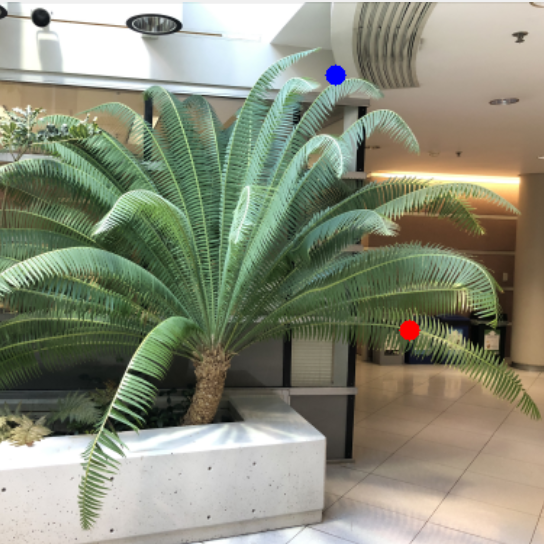
Seunghyeon Seo, Yeonjin Chang, Nojun Kwak ICCV 2023 project page / arXiv We utilize the flipped reflection rays as additional training resources for the few-shot novel view synthesis, leading to more accurate surface normal estimation. |
|
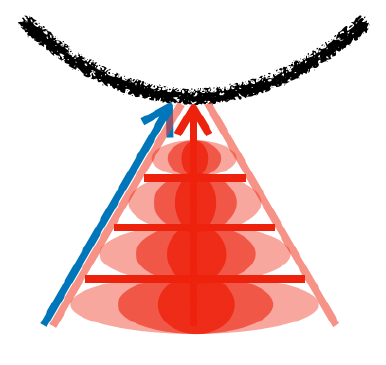
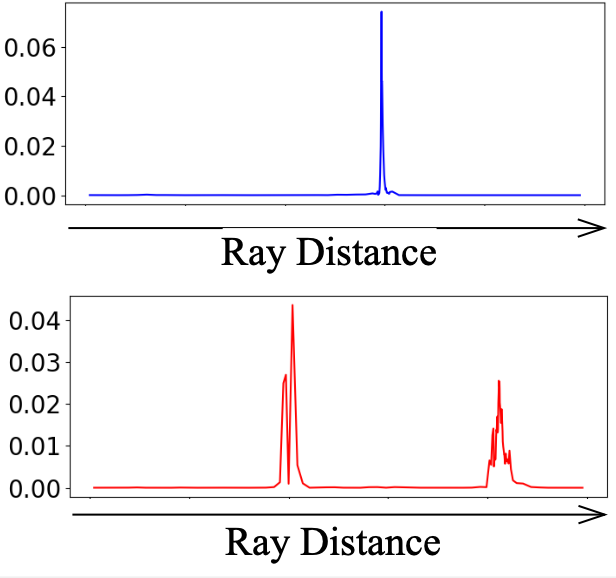
Seunghyeon Seo, Donghoon Han*, Yeonjin Chang*, Nojun Kwak CVPR 2023 project page / arXiv We model a ray with mixture density model, leading to efficient learning of density distribution with sparse inputs, and propose an effective auxiliary task of ray depth estimation for few-shot novel view synthesis. |
 
|
Jookyung Song, Yeonjin Chang*, Seonguk Park, Nojun Kwak ICASSP 2023 arXiv Write short description here. |